
Cannabis has long been a subject of intrigue and controversy, often overshadowed by its psychoactive effects and legal status. However, as research delves deeper, we are beginning to understand the complex chemistry of cannabis and its potential therapeutic benefits. One such compound that has gained attention in recent years is Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid (THCA), a non-psychoactive precursor to the well-known Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). This article aims to demystify THCA, exploring its nature, benefits, and its distinct role in the cannabis plant.
The Basics of Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid
It is a cannabinoid, a type of compound found in the cannabis plant, often reffered to as “thca flower”. Unlike THC, it is non-psychoactive, which means it does not produce the ‘high’ associated with cannabis use. This is primarily because it does not effectively bind to the CB1 receptors in the brain, which are responsible for the psychoactive effects of THC. THCA is found in raw and live cannabis, and it converts to THC when exposed to heat – a process known as decarboxylation.
Chemical Structure and Decarboxylation
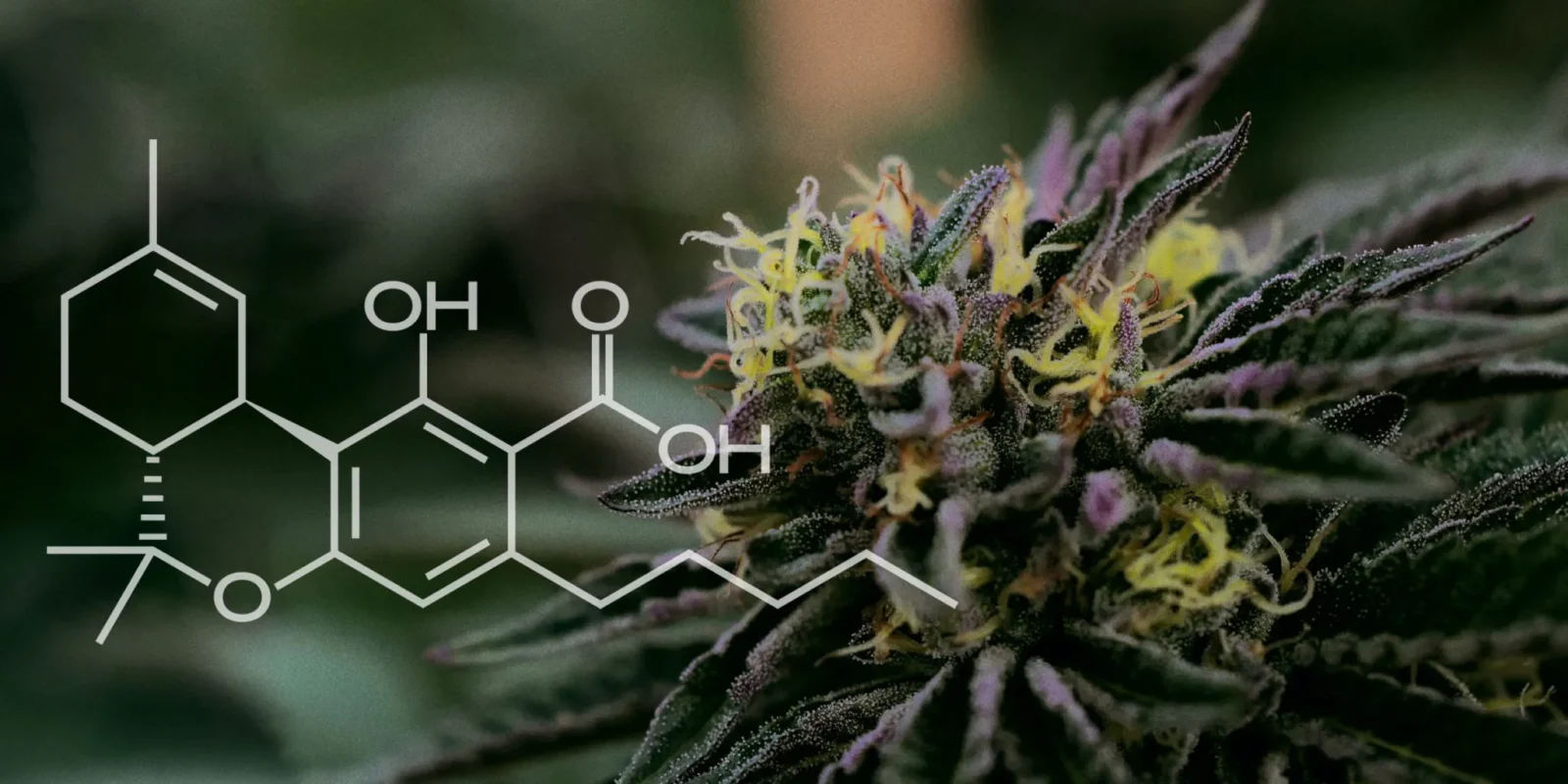
The chemical structure of it is similar to THC, but with a crucial difference: THCA contains an additional carboxyl group. This group is lost during decarboxylation, transforming Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid into THC. Decarboxylation can occur through various methods, including smoking, vaporizing, or cooking cannabis. The process is not only crucial for those seeking the psychoactive effects of THC but also impacts the efficacy and type of therapeutic benefits the compound might offer.
Potential Therapeutic Benefits
While much of the research on cannabis has focused on THC and CBD (cannabidiol), emerging studies suggest that it has its own unique therapeutic properties. These include anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-proliferative effects. For instance, some studies have suggested that THCA may help reduce inflammation, making it potentially beneficial for conditions like arthritis and lupus. Its neuroprotective properties might also make it useful in treating neurodegenerative diseases.
THCA in the Plant’s Life Cycle

In the life cycle of the cannabis plant, it plays a crucial role. It serves as a form of defense against pests and ultraviolet radiation. The high concentration of Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid in young cannabis plants contributes to their survival and growth. As the plant matures, the levels of THCA and other cannabinoids change, influenced by factors like light, temperature, and genetics.
Extraction and Consumption
Extracting from cannabis requires careful consideration of temperature and technique, as excessive heat can convert THCA to THC. Various extraction methods, including cold-water extraction and certain solvent-based techniques, are designed to preserve the Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid content. When it comes to consumption, raw cannabis, such as in juices or salads, is a popular way to ingest THCA. Additionally, its tinctures are also gaining popularity for their ease of use and dosage precision.
Legal Status and Research
The legal status is complex and varies by region. In many places, cannabis laws focus on THC, leaving a grey area regarding THCA. However, as research continues and the potential therapeutic benefits are become clearer, there is a growing call for legal frameworks to adapt accordingly. It’s important for consumers and patients to stay informed about the legal status and related products in their jurisdiction.
Challenges in Research

The exploration of Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid’s properties and potential is not without its challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the legal status of cannabis in many regions, which can hinder scientific research. Furthermore, the instability of THCA, which easily converts to THC when exposed to heat or prolonged storage, poses difficulties in handling and studying the compound. This instability necessitates precise methodologies to ensure the integrity of research findings.
THCA vs. THC: Understanding the Differences
It is crucial to distinguish between THCA and THC, as their effects on the human body are markedly different. While THC is known for its psychoactive properties, Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid does not produce these effects. This distinction is especially important for medical users of cannabis who seek the therapeutic benefits without the psychoactive experience. Understanding this difference also aids in the development of targeted treatments that harness the specific benefits of each cannabinoid.
Role in the Entourage Effect
The entourage effect is a theory suggesting that the various compounds in cannabis work together synergistically, enhancing each other’s effects. THCA, along with other cannabinoids and terpenes, is believed to contribute to this phenomenon. The presence of Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid in a cannabis product could potentially alter or enhance the therapeutic outcome, emphasizing the importance of considering the entire cannabinoid profile in medicinal cannabis formulations.
Safety and Side Effects

While THCA is considered non-psychoactive and generally safe, it is important to understand its potential side effects. Research into the side effects of THCA is limited, but as with any compound, reactions can vary from person to person. Patients and consumers should approach Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid with the same caution as other cannabinoids, particularly in terms of dosage and interactions with other medications.
Pharmacological Potential of THCA
The pharmacological aspects of THCA are a growing area of interest. Its potential to interact with various biological systems, including the endocannabinoid system, opens up possibilities for therapeutic applications. Research into the pharmacokinetics (how the body processes the compound) and pharmacodynamics (how the compound affects the body) of THCA is crucial for developing effective and safe cannabis-based treatments.
THCA in Consumer Products
With increasing interest in Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid, its presence in consumer cannabis products is expanding. Products specifically designed to maintain high levels of THCA are appearing on the market, including THCA-rich oils, capsules, and topicals. These products are often marketed for their potential health benefits, appealing to consumers interested in the therapeutic aspects of cannabis without the psychoactive effects.
Concluding Thoughts on THCA
THCA represents an exciting and relatively untapped area of cannabis research. Its unique properties and potential therapeutic benefits set it apart from more well-known cannabinoids like THC and CBD. As research continues and our understanding deepens, THCA could become a key component in the medicinal cannabis landscape, offering new avenues for treatment and a deeper understanding of the complex cannabis plant.









