
Wherever you run any business, income tax applies to your company’s investment income. The tariff fee varies in different provinces, and it is necessary to follow all the regulations to get rid of the yearly headaches. Sometimes, it is challenging for a few individuals to calculate the exact corporate taxation rate.
Even if you are running a small-scale business or have a small income, clearing all your tax debts is a must. Like every province, Canada has different regulations on income liability for companies. It can affect your company; therefore, you must know everything about the federal fees, old data, CPCC, gains, and other necessary details of tax rates.
If you are not good at calculating the exact rate, you must hire a consultant who can help you understand Canadian tax regulations and imposed rates. This write-up will help us understand the investment earning tax and how it is calculated in Canada.
About Canadian Tax Fee for Businesses

The tax fee for different businesses in Canada may differ depending on the organization’s revenue, income, location, etc. It applies to all types of businesses. But a few of them are exempted from the applicable obligation in different states of Canada, like Hutterite, charities, crown-based corporations, etc.
In Canada, two types of federal fees exist, also called the dual taxation rate. For small-scale companies, the rate is quite lower, i.e., 9%. But it is necessary to satisfy some requirements to be applicable for such rates. When it comes to any company tax fee for big businesses, then it is quite high, i.e., 38%.
Generally, the federal fee is 10%, and the other 13% is the general taxation reduction. The left 15% is the net tax applicable to other general corporations. Depending on the different provinces, the rate may differ.
The taxation is also applicable based on gains, income, as well as dividends. You must understand each category carefully to calculate the exact income tax. Further, you will get detailed information on corporate investment income tax rate for different companies.
Federal Tax for Canadian Corporates

t along with private companies managed by Canadian non-residents. All types of processing, as well as manufacturing companies, are also included and applicable to this tax.
For all the companies, the basic fee is 38%, which includes a federal decrease of 10%, a general taxation reduction of 13%, and a liability rate for corporations of 15%. There is a specific income limit for-scale small businesses. If any company’s income goes beyond the small business’s threshold limit, it will apply to the general taxation rate.
Liability Fee for Canadian Small-scale Business Companies
The taxation of every small business in any state of Canada depends on its revenue as well as structure. With the help of SBD, CCPCs reduce the tax on the active incomes of their businesses. The current limit is set, i.e., $500000 for almost every territory and province. In every situation, the corporate needs to pay the government.
There is a possibility of changes in the rate every year due to the change in the company’s revenue that may go above or below the SBD threshold. The rate can be affected; hence, you must keep checking the calculations frequently. The tax deduction helps many start-ups and small businesses meet their tax obligations. It benefits big companies by providing incentives.
Tax Rates Available in Canada for Company’s Capital Gains

Capital gain depicts the profit any company can obtain by selling its passive assets, such as stocks, land, property, businesses, etc. It is necessary to involve the gain in the company’s taxable income. Including half of the company’s capital gain in an income is essential, also called the inclusion rate.
If you include half of your gains, the taxation rate will also be 50% of your investment earnings. If your organization involves gains, hiring a consultant who can help you manage your sales and understand overall gains is necessary. By using losses, different corporations can easily outweigh their gains.
Taxation Rate for Companies in Canada
Earnings come from gains, rentals, etc., are not direct income from any business and are considered passive income. But it affects overall income, and a company must pay taxes. In different states of Canada, if one’s passive income goes beyond $50000, one has to pay more tax than other ordinary small-scale business people.
The purpose of this legislation is to invest passive income in any company and not to grow more. The taxable fee is low on such an income source.
Province Corporate Taxation Rates in Canada
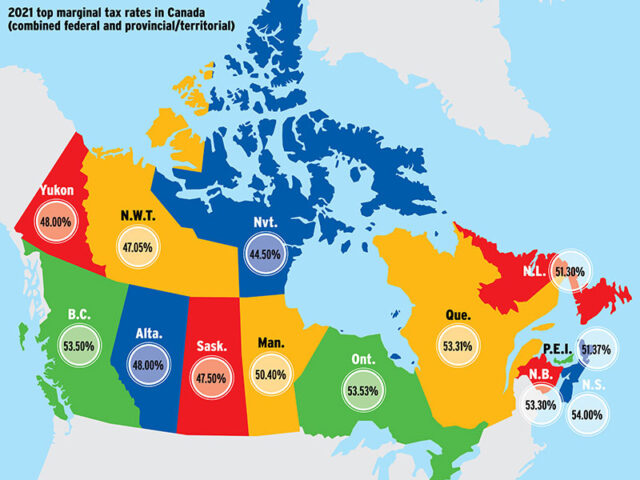
For various businesses, the tax fee is either low or high and may vary as per different provinces. Small companies with SBD less than the available threshold limit must pay comparatively less tax.
The mentioned limit in different states of Canada is $500000. For all types of income sources, the high taxation rate is quite applicable. The taxable rate is different in Alberta and Quebec. These provinces do not have agreements as per the CRA.
Calculator for Calculating the Company’s Tax

It is necessary to understand the finances of a company before calculating the tax fee. You must keep regulations, i.e., federal as well as provincial, in your mind. Many calculators are available commercially, but you cannot expect to get accurate results.
Instead of getting confused, you must hire an expert CPA to calculate the accurate tax accurately. In case of miscalculation, you need to pay penalties. Therefore, you must always consult an accountant to make plans and calculate the company’s income liability.
The Bottom Line
In Canada, the tax on any corporate investment income may differ from other countries and provinces. It is necessary to understand Canada’s tax regulations and calculate the rate accurately with the help of an accountant.









